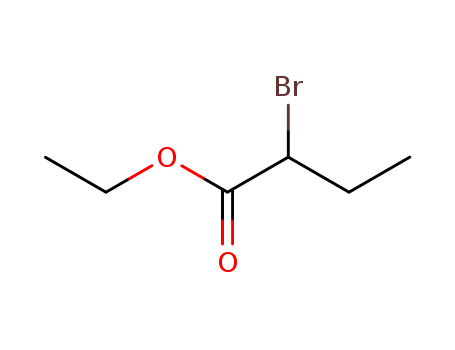
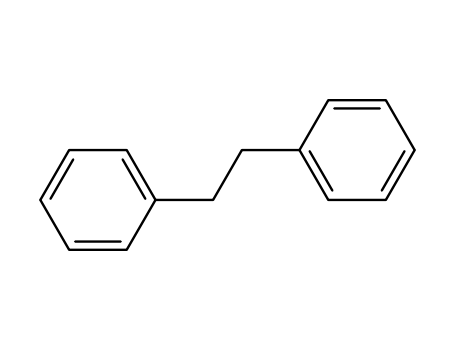
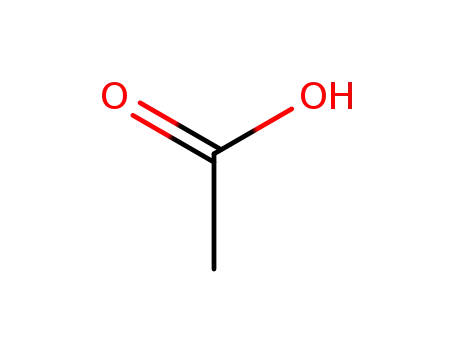
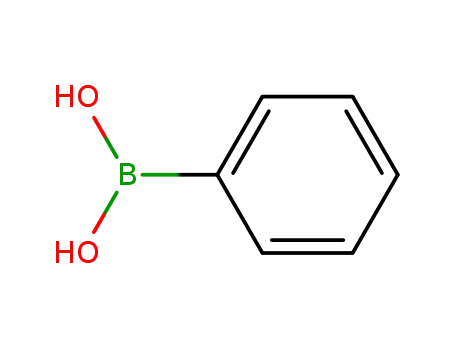
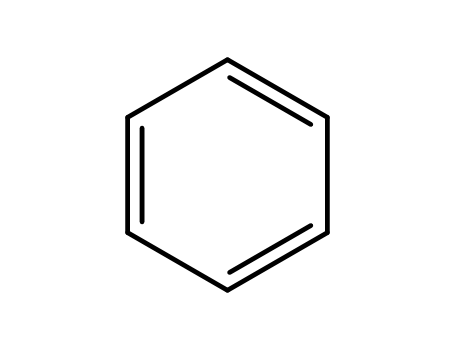
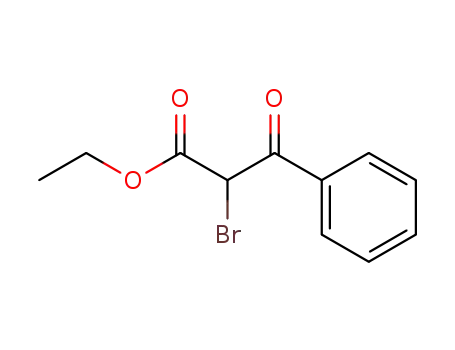
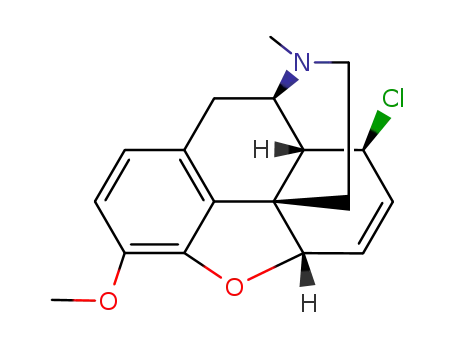
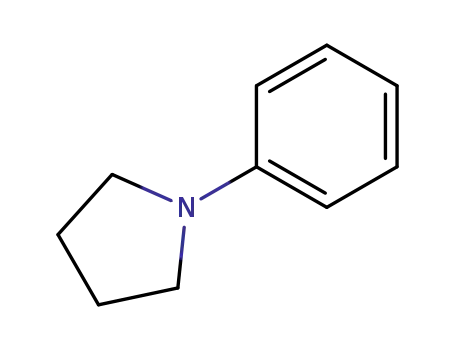
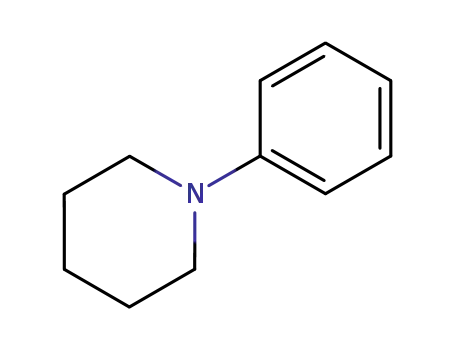
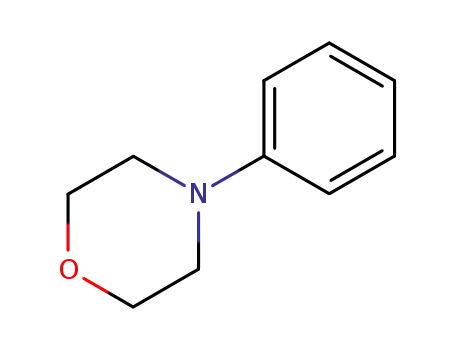
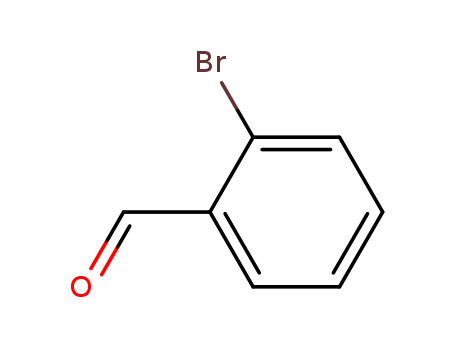
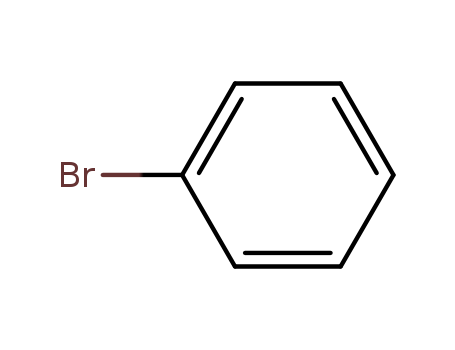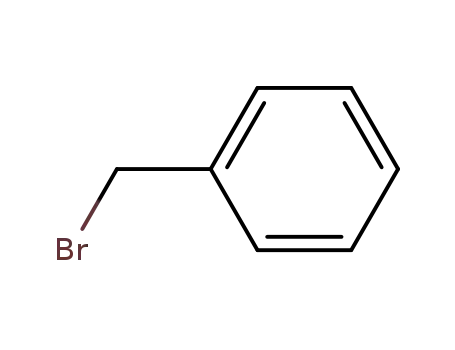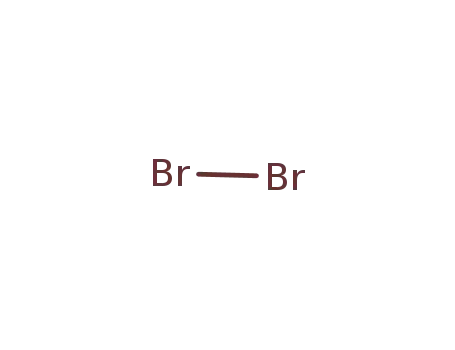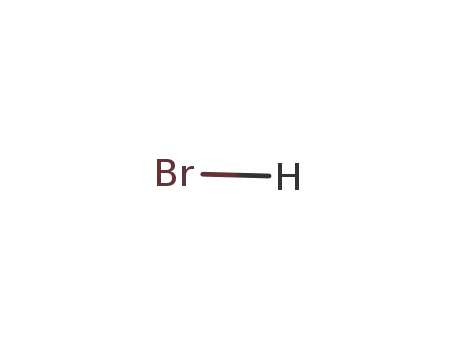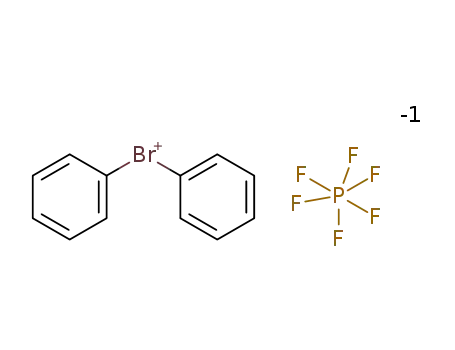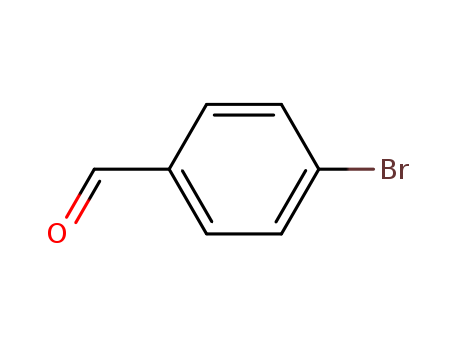Comments on a Conversion of Epoxides to Halohydrins with Elemental Halogen Catalyzed by Phenylhydrazine: Tandem Electrophilic Halogenation of Aromatic Compounds and Epoxide Ring Opening to Halohydrins
Soroka, Miroslaw,Goldeman, Waldemar,Malysa, Piotr,Stochaj, Monika
, p. 2341 - 2344 (2003)
The halogenation of aromatic compounds b...
A convenient new method for the bromination of deactivated aromatic compounds
Duan, Jianxin,Zhang, Lian Hao,Dolbier Jr., William R.
, p. 1245 - 1246 (1999)
Treatment of deactivated aromatic compou...
Photoelectrochemistry with Quinone Radical Anions-Photoassisted Reduction of Halobenzenes and Carbonyl Compounds
Robertson, Peter K. J.,Eggins, Brian R.
, p. 1829 - 1832 (1994)
Photoexcited electrochemically generated...
C?I-Selective Cross-Coupling Enabled by a Cationic Palladium Trimer
Diehl, Claudia J.,Scattolin, Thomas,Englert, Ulli,Schoenebeck, Franziska
, p. 211 - 215 (2019)
While there is a growing interest in har...
Directly Observed Reductive Elimination of Aryl Halides from Monomeric Arylpalladium(II) Halide Complexes
Roy, Amy H.,Hartwig, John F.
, p. 13944 - 13945 (2003)
Monomeric, three-coordinate arylpalladiu...
Vibrational Spectroscopy and Photodissociation Properties of Ions As Determined by Two-Laser Photodissociation Techniques.
Honovich, Jeffrey P.,Dunbar, Robert C.
, p. 3755 - 3758 (1983)
Iodobenzene, bromobenzene, and m-iodotol...
Effects of Solvent and Additives on the Rearrangement Pathway of the Seyferth Reaction
Lambert, Joseph B.,Boch, Richard J.,Larson, Eric G.
, p. 3054 - 3059 (1985)
The Seyferth reagent has dual reactivity...
A study on Zr-Ir multiple bonding active for C-H bond cleavage
Oishi, Masataka,Oshima, Masato,Suzuki, Hiroharu
, p. 6634 - 6654 (2014)
Zr-Ir hydrido complexes with ansa-(cyclo...
The Addition Reaction of Benzynes Generated Electrochemically from Dihalobenzenes with Tertiary Amines
Egashira, Naoyoshi,Takenga, Jun,Hori, Fumikai
, p. 2671 - 2673 (1987)
The electroreduction of dihalobenzenes w...
ON THE ABSOLUTE REACTIVITY OF ARYL CATIONS: SELECTIVITY TOWARD HALIDE IONS AS A FUNCTION OF VISCOSITY
Lorand, John P.
, p. 7337 - 7340 (1989)
The selectivities toward bromide and chl...
Generation, structure, and reactivity of o-iodobenzoyloxyl radicals. Pulsed laser photolysis of 1-(o-halobenzoyloxy)-2-pyridones
Hashimoto, Ji-Ichiro,Segawa, Katsunori,Itoh, Hiroki,Sakuragi, Hirochika
, p. 362 - 363 (2000)
The transient absorption spectrum of o-i...
Photochemically Switching Diamidocarbene Spin States Leads to Reversible Büchner Ring Expansions
Perera, Tharushi A.,Reinheimer, Eric W.,Hudnall, Todd W.
, p. 14807 - 14814 (2017)
The discovery of thermal and photochemic...
Nucleophilic substitution of hydrogen in naphthalene by chloride (Cl -) in ionic liquids
Shi, Shen Yi,Kong, Ai Guo,Zhao, Xin Hua,Ding, Han Ming,Yang, Fan,Shan, Yong Kui
, p. 147 - 150 (2011)
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution of hy...
Hydroxyl radical induced reactions in aqueous solutions of halogenated benzenes: Effect of electronegativity of halogen
Mohan, Hari,Mittal, Jai P.
, p. 599 - 607 (2002)
The .OH radicals, generated by radiolysi...
Cope rearrangement versus a novel tandem retro-diels-alder-diels-alder reaction with role reversal
Su, Kuan-Jen,Mieusset, Jean-Luc,Arion, Vladimir B.,Brecker, Lothar,Brinker, Udo H.
, p. 113 - 115 (2007)
A reinvestigation of the thermolysis of ...
REDUCTION BY A MODEL OF NAD(P)H. 42. DIRECT EVIDENCE FOR ONE ELECTRON TRANSFER MECHANISM IN THE REDUCTION OF ARENEDIAZONIUM SALTS.
Yasui, Shinro,Nakamura, Kaoru,Ohno, Atsuyoshi
, p. 3331 - 3334 (1983)
Arenediazonium salts are reduced by an N...
Through-Space Activation Can Override Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Guan, Liangyu,Holl, Maxwell Gargiulo,Pitts, Cody Ross,Struble, Mark D.,Siegler, Maxime A.,Lectka, Thomas
, p. 14913 - 14916 (2017)
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS...
-
Ainley,Challenger
, p. 2171,2176 (1930)
-
-
Beringer et al.
, p. 141,143 (1956)
-
Bromination of Deactivated Aromatics Using Potassium Bromate
Harrison, J.J.,Pellegrini, J.P.,Selwitz, C.M.
, p. 2169 - 2171 (1981)
-
Pd-catalyzed reduction of aryl halides using dimethylformamide as the hydride source
Zawisza, Anna Maria,Muzart, Jacques
, p. 6738 - 6742 (2007)
The Pd-catalyzed homocoupling of aryl ha...
-
Summers,Larson
, p. 4498 (1952)
-
Properties of PTFE tape as a semipermeable membrane in fluorous reactions
Parsons, Brendon A.,Smith, Olivia Lin,Chae, Myeong,Dragojlovic, Veljko
, p. 980 - 993 (2015)
In a PTFE tape phase-vanishing reaction ...
Bromine and iodine-cucurbit[6]uril complexes: Preparation and applications in synthetic organic chemistry
Reddy,Cavallini,Demets,Silva
, p. 2262 - 2264 (2014)
Iodine and bromine inclusion compounds w...
-
Leicester
, p. 619 (1938)
-
-
Henry
, p. 1886,1888 (1971)
-
Photochemical Decomposition of Dibenzoyl Peroxide and Phenyl Benzoate in Solid KBr Matrix
Owen, David J.,O'Donnell, Jennifer,Schutt, Wendy,Morrow, Jeffrey,Li, Yuzhuo
, p. 6203 - 6207 (1993)
Physical and photochemical properties of...
-
Bunnett et al.
, p. 367 (1966)
-
-
Kohn,Mueller
, p. 407 (1909)
-
-
Rice,Morganroth
, p. 1388 (1956)
-
Noncatalytic bromination of benzene: A combined computational and experimental study
Shernyukov, Andrey V.,Genaev, Alexander M.,Salnikov, George E.,Rzepa, Henry S.,Shubin, Vyacheslav G.
, p. 210 - 225 (2016)
The noncatalytic bromination of benzene ...
-
Le Fevre,Markham
, p. 703 (1934)
-
Formation and Reactivity of the Radical Cation of Bromobenzene in Aqueous Solution: A Pulse Radiolysis Study
Mohan, Hari,Mittal, Jai P.
, p. 6519 - 6524 (1995)
A transient optical absorption band (λma...
-
Huyser,Wang
, p. 3901 (1968)
-
Radical Rearrangements of Bicyclohexane: Homolytic Substitution of a Cyclobutane Ring
Walton, John C.
, p. 1252 - 1254 (1987)
Bromine atoms react with bicyclohexane i...
Remarkably stable ortho-halophenylcopper reagents
Ebert, Greg W.,Pfennig, Deborah R.,Suchan, Scott D.,Donovan Jr., Thomas A.
, p. 2279 - 2282 (1993)
We wish to report the generation of rema...
Reactivity of alkali and alkaline earth metal tetrafluorobromates towards aromatic compounds and pyridine
Sobolev, Vasily I.,Filimonov, Victor D.,Ostvald, Roman V.,Radchenko, Vyacheslav B.,Zherin, Ivan I.
, p. 120 - 123 (2016)
The bromination activity of tetrafluorob...
-
Kohn,Fink
, p. 187 (1923)
-
Silk?Fibroin-Supported Palladium Catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and Ullmann Coupling Reactions of Aryl Chlorides
Albano, Gianluigi,Farinola, Gianluca M.,Giannini, Cinzia,Musio, Roberta,Omenetto, Fiorenzo G.,Rizzo, Giorgio,Sibillano, Teresa
supporting information, (2022/02/03)
Recently, we have reported the preparati...
Radical Hydrodehalogenation of Aryl Halides with H2 Catalyzed by a Phenanthroline-Based PNNP Cobalt(I) Complex
Iizuka, Kosuke,Ishizaka, Yusuke,Jheng, Nai-Yuan,Minami, Yasunori,Naganawa, Yuki,Nakajima, Yumiko,Sekiguchi, Akira
, p. 2320 - 2329 (2022/02/16)
Radical hydrodehalogenation of aryl hali...
Alternative method for the synthesis of triazenes from aryl diazonium salts
Abrams
, (2021/05/10)
An alternative mild method for access to...
METHOD FOR PRODUCING LITHIUM COMPOUND
-
Paragraph 0044; 0072-0092, (2021/01/29)
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a metho...
 English
English 中文
中文
 English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego